MDdMD Conformational Transitions -- About
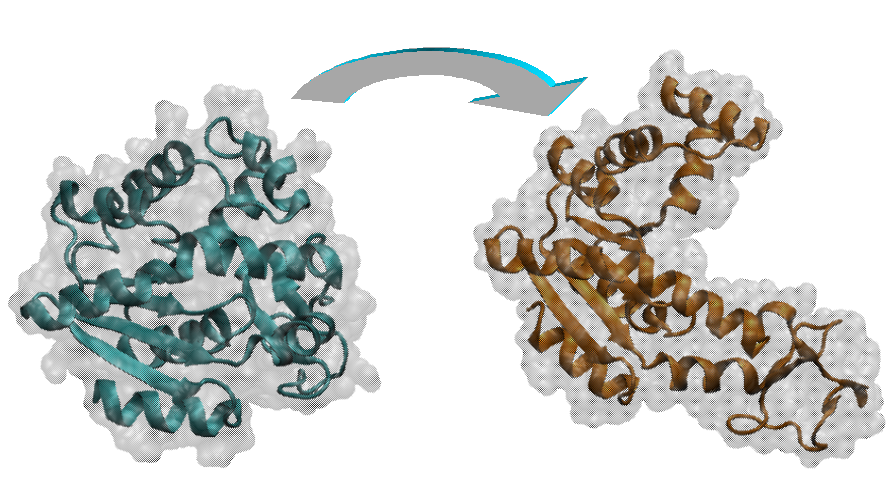
MDdMD is a new method for determining pathways for conformational transitions in macromolecules based on the use of discrete molecular dynamics and biasing techniques based on a combination of essential dynamics and Maxwell-Demon sampling techniques. The method can work with high efficiency at different levels of resolution, including the atomistic one, and can help to define initial pathways for further exploration by means of more accurate atomistic molecular dynamics simulations.
Related Molecular Modeling and Bioinformatics Group Servers:
More than 1700 trajectories of proteins representative of monomeric soluble structures in the protein data bank (PDB) have been obtained by means of state-of-the-art atomistic molecular dynamics simulations in near-physiological conditions. The trajectories and analyses are stored in a large data warehouse, which can be queried for dynamic information on proteins, including interactions. Here, we describe the project and the structure and contents of our database, and provide examples of how it can be used to describe the global flexibility properties of proteins. Basic analyses and trajectories stripped of solvent molecules at a reduced resolution level are available from our web server.

FlexServ is a web-based tool for the analysis of protein flexibility. The server incorporates powerful protocols for the coarse-grained determination of protein dynamics using different versions of Normal Mode Analysis (NMA), Brownian dynamics (BD) and Discrete Dynamics (DMD). It can also analyze user provided trajectories. The server allows a complete analysis of flexibility using a large variety of metrics, including basic geometrical analysis, B-factors, essential dynamics, stiffness analysis, collectivity measures, Lindemann's indexes, residue correlation, chain-correlations, dynamic domain determination, hinge point detections, etc. Data is presented through a web interface as plain text, 2D and 3D graphics.

MDWeb and MDMoby constitute a web-based platform to help access to molecular dynamics (MD) in the standard and high-throughput regime. The platform provides tools to prepare systems from PDB structures mimicking the procedures followed by human experts. It provides inputs and can send simulations for three of the most popular MD packages (Amber, NAMD and Gromacs). Tools for analysis of trajectories, either provided by the user or retrieved from our MoDEL database (http://mmb.irbbarcelona.org/MoDEL) are also incorporated. The platform has two ways of access, a set of web-services based on the BioMoby framework (MDMoby), programmatically accessible and a web portal (MDWeb).