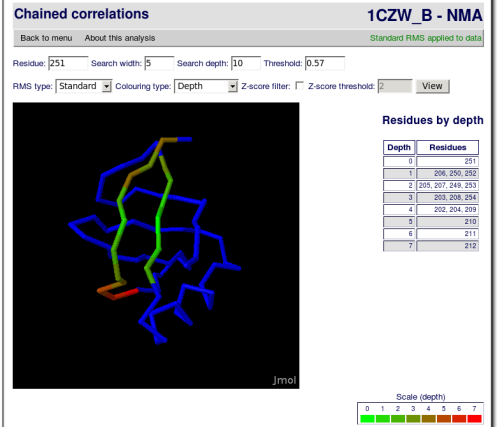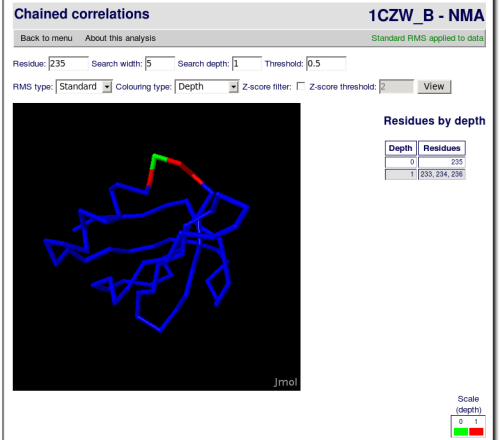
This is a post-processing of the raw correlations analysis, where far correlations can be found through intermediate correlations.
The procedure followed to perform this search is as follows. A root residue must be selected. the search will be of residues correlated to the root residue. A correlation threshold must be provided, and is used to filter not correlated residues. If the correlation between the search residue and the candidate residue is below the threshold, the candidate is not considered. The search width value is the number of residues that will be selected among the accepted candidates. The selected residues will be the ones with the higher correlation.
With this data, a search step can be performed and a set of residues correlated to the first one is produced.

The search depth parameters is the number of times that this search will be performed. Each time the algorithm is repeated, the root residues are the results of the previous iteration. The results of each iteration are correlated with the previous ones, but they may have lower correlations with the first root residue.
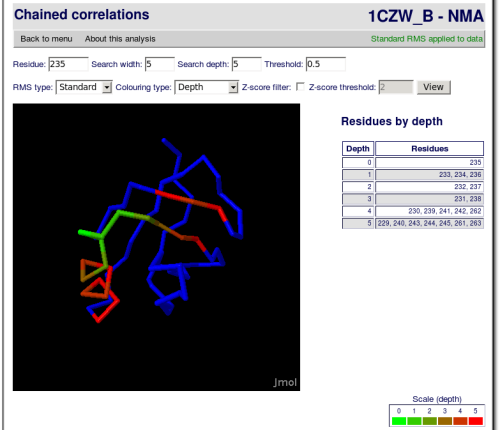
Using this iterative approach, a chain of correlated residues can be built, allowing the researcher to find distant correlations that are not directly perceived.
The results will be given visually colour-coded with a JMol applet. There will also be a table enumerating the different residues found in each step of the search
In all cases additional filter can be applied by comparing the found correlation to that expected for the inter-residue distance in a set of proteins which were analyzed by accurate atomistic molecular dynamics simulations (see the raw correlations analysis).