Automatic Ligand parameterization tutorial using BioExcel Building Blocks
Automatic Ligand parameterization tutorial using BioExcel Building Blocks (biobb)
This tutorial aims to illustrate the process of ligand parameterization for a small molecule, step by step, using the BioExcel Building Blocks library (biobb). The particular example used is the Ibuprofen small compound (3-letter code IBP, Drugbank code DB01050), a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) derived from propionic acid and it is considered the first of the propionics.
OpenBabel and ACPype packages are used to add hydrogens, energetically minimize the structure, and generate parameters for the GROMACS package. With Generalized Amber Force Field (GAFF) forcefield and AM1-BCC charges.
Biobb modules used:
- biobb_io: Tools to fetch data to be consumed by the rest of the Biobb building blocks.
- biobb_chemistry: Tools to manipulate chemistry data.
Auxiliary libraries used
- jupyter: Free software, open standards, and web services for interactive computing across all programming languages.
- nglview: Jupyter/IPython widget to interactively view molecular structures and trajectories in notebooks.
Conda Installation and Launch
git clone https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_wf_ligand_parameterization.git
cd biobb_wf_ligand_parameterization
conda env create -f conda_env/environment.yml
conda activate biobb_wf_ligand_parameterization
jupyter-notebook biobb_wf_ligand_parameterization/notebooks/biobb_wf_ligand_parameterization.ipynb
Pipeline steps:
- Input Parameters
- Fetching Ligand Structure
- Add Hydrogen Atoms
- Energetically Minimize Hydrogen Atoms
- Generating Ligand Parameters
- Output Files
- Questions & Comments

Initializing colab
The two cells below are used only in case this notebook is executed via Google Colab. Take into account that, for running conda on Google Colab, the condacolab library must be installed. As explained here, the installation requires a kernel restart, so when running this notebook in Google Colab, don't run all cells until this installation is properly finished and the kernel has restarted.
# Only executed when using google colab
import sys
if 'google.colab' in sys.modules:
import subprocess
from pathlib import Path
try:
subprocess.run(["conda", "-V"], check=True)
except FileNotFoundError:
subprocess.run([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", "condacolab"], check=True)
import condacolab
condacolab.install()
# Clone repository
repo_URL = "https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_wf_ligand_parameterization.git"
repo_name = Path(repo_URL).name.split('.')[0]
if not Path(repo_name).exists():
subprocess.run(["mamba", "install", "-y", "git"], check=True)
subprocess.run(["git", "clone", repo_URL], check=True)
print("⏬ Repository properly cloned.")
# Install environment
print("⏳ Creating environment...")
env_file_path = f"{repo_name}/conda_env/environment.yml"
subprocess.run(["mamba", "env", "update", "-n", "base", "-f", env_file_path], check=True)
print("🎨 Install NGLView dependencies...")
subprocess.run(["mamba", "install", "-y", "-c", "conda-forge", "nglview==3.0.8", "ipywidgets=7.7.2"], check=True)
print("👍 Conda environment successfully created and updated.")
# Enable widgets for colab
if 'google.colab' in sys.modules:
from google.colab import output
output.enable_custom_widget_manager()
# Change working dir
import os
os.chdir("biobb_wf_ligand_parameterization/biobb_wf_ligand_parameterization/notebooks")
print(f"📂 New working directory: {os.getcwd()}")
Input parameters
Input parameters needed:
- ligandCode: 3-letter code of the ligand structure (e.g. IBP, Drugbank code DB01050)
- mol_charge: Molecule net charge (e.g. -1)
- pH: Acidity or alkalinity for the small molecule. Hydrogen atoms will be added according to this pH. (e.g. 7.4)
import nglview
import ipywidgets
import os
ligandCode = 'IBP'
mol_charge = -1
pH = 7.4
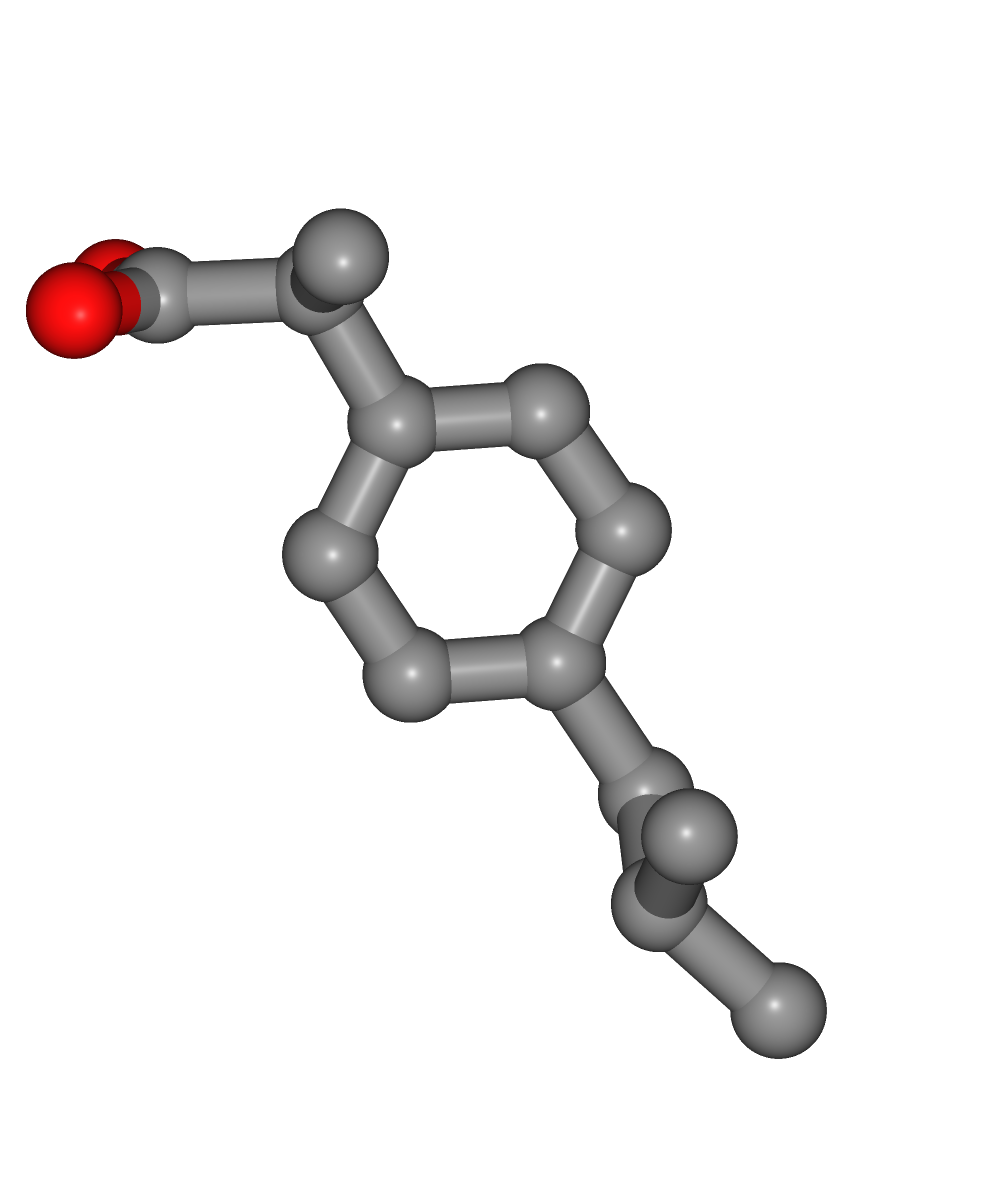
Fetching ligand structure
Downloading ligand structure in PDB format from the IRB PDB MIRROR database.
Alternatively, a PDB file can be used as starting structure.
Building Blocks used:
- Ligand from biobb_io.api.ligand
# Ligand: Download ligand structure from MMB PDB mirror REST API (https://mmb.irbbarcelona.org/api/)
# Import module
from biobb_io.api.ligand import ligand
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
input_structure = ligandCode + '.pdb'
prop = {
'ligand_code' : ligandCode
}
#Create and launch bb
ligand(output_pdb_path=input_structure,
properties=prop)
#Show small ligand structure
view = nglview.show_structure_file(input_structure)
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='all')
view._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','300px'])
view.camera='orthographic'
view

Add Hydrogen Atoms
Adding Hydrogen atoms to the small molecule, according to the given pH.
Building Blocks used:
- BabelAddHydrogens from biobb_chemistry.babelm.babel_add_hydrogens
# Babel_add_hydrogens: add Hydrogen atoms to a small molecule
# Import module
from biobb_chemistry.babelm.babel_add_hydrogens import babel_add_hydrogens
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_babel_h = ligandCode + '.H.mol2'
prop = {
'ph' : pH,
'input_format' : 'pdb',
'output_format' : 'mol2'
}
#Create and launch bb
babel_add_hydrogens(input_path=input_structure,
output_path=output_babel_h,
properties=prop)
#Show small ligand structure
view = nglview.show_structure_file(output_babel_h)
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='all')
view.camera='orthographic'
view

Energetically minimize Hydrogen Atoms
Energetically minimize newly added Hydrogen atoms.
Building Blocks used:
- BabelMinimize from biobb_chemistry.babelm.babel_minimize
# Babel_minimize: Structure energy minimization of a small molecule after being modified adding hydrogen atoms
# Import module
from biobb_chemistry.babelm.babel_minimize import babel_minimize
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_babel_min = ligandCode + '.H.min.pdb'
prop = {
'method' : 'sd',
'criteria' : '1e-10',
'force_field' : 'GAFF'
}
#Create and launch bb
babel_minimize(input_path=output_babel_h,
output_path=output_babel_min,
properties=prop)
#Show small ligand structure
view = nglview.show_structure_file(output_babel_min)
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='all')
view._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','300px'])
view.camera='orthographic'
view
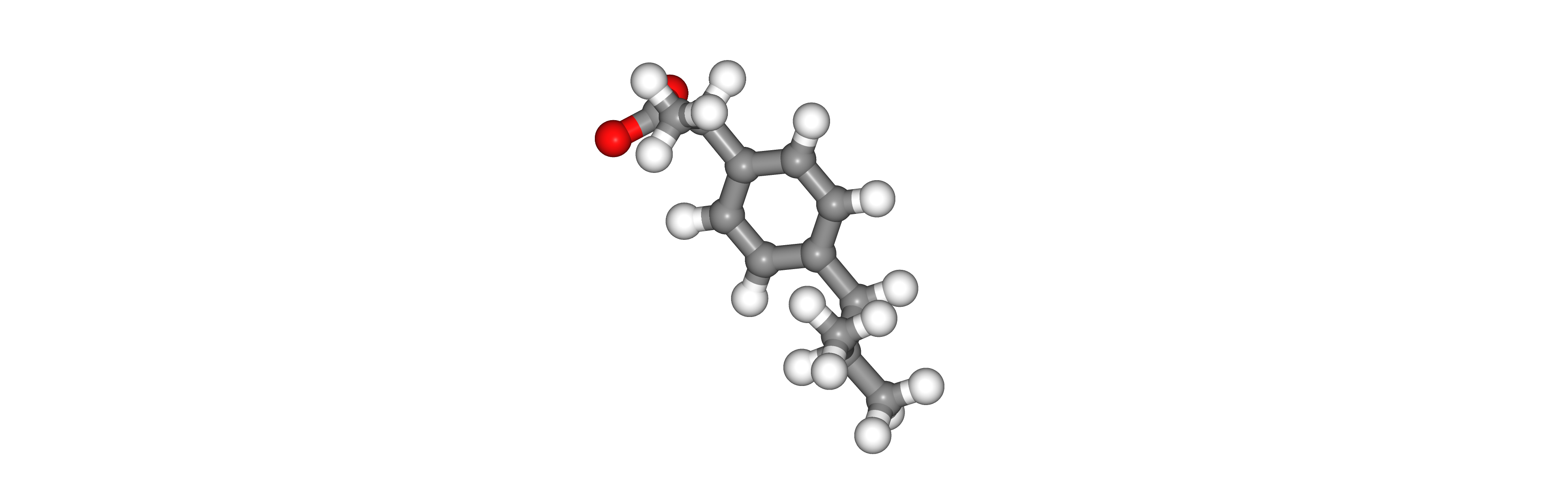
#Show different structures generated (for comparison)
view1 = nglview.show_structure_file(input_structure)
view1.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick')
view1._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['250px','300px'])
view1.camera='orthographic'
view1
view2 = nglview.show_structure_file(output_babel_h)
view2.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick')
view2._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['250px','300px'])
view2.camera='orthographic'
view2
view3 = nglview.show_structure_file(output_babel_min)
view3.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick')
view3._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['250px','300px'])
view3.camera='orthographic'
view3
ipywidgets.HBox([view1, view2, view3])


Generating ligand parameters
Building GROMACS topology corresponding to the ligand structure.
Force field used in this tutorial step is amberGAFF: General AMBER Force Field, designed for rational drug design.
Building Blocks used:
- AcpypeParamsGMX from biobb_chemistry.acpype.acpype_params_gmx
# Acpype_params_gmx: Generation of topologies for GROMACS with ACPype
# Import module
from biobb_chemistry.acpype.acpype_params_gmx import acpype_params_gmx
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_acpype_gro = ligandCode + 'params.gro'
output_acpype_itp = ligandCode + 'params.itp'
output_acpype_top = ligandCode + 'params.top'
output_acpype = ligandCode + 'params'
prop = {
'basename' : output_acpype,
'charge' : mol_charge
}
#Create and launch bb
acpype_params_gmx(input_path=output_babel_min,
output_path_gro=output_acpype_gro,
output_path_itp=output_acpype_itp,
output_path_top=output_acpype_top,
properties=prop)
#Show small ligand structure
view = nglview.show_structure_file(output_acpype_gro)
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='all')
view._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','300px'])
view.camera='orthographic'
view

Output files
Important Output files generated:
- output_acpype_gro (IBPparams.gro): Structure of the parameterized ligand in gro (GROMACS) format.
- output_acpype_top (IBPparams.top): Topology of the parameterized ligand, including a reference to the IBPparams.itp.
- output_acpype_itp (IBPparams.itp): Include Topology File (itp) of the parameterized ligand, including the parameters information: bonds, angles, dihedrals, etc.
