Protein MD Setup tutorial using BioExcel Building Blocks
Protein MD Setup tutorial using BioExcel Building Blocks (biobb)
Based on the official GROMACS tutorial: http://www.mdtutorials.com/gmx/lysozyme/index.html
This tutorial aims to illustrate the process of setting up a simulation system containing a protein, step by step, using the BioExcel Building Blocks library (biobb). The particular example used is the Lysozyme protein (PDB code 1AKI, https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb1AKI/pdb).
Settings
Biobb modules used
- biobb_io: Tools to fetch biomolecular data from public databases.
- biobb_model: Tools to model macromolecular structures.
- biobb_gromacs: Tools to setup and run Molecular Dynamics simulations.
- biobb_analysis: Tools to analyse Molecular Dynamics trajectories.
Auxiliary libraries used
- jupyter: Free software, open standards, and web services for interactive computing across all programming languages.
- nglview: Jupyter/IPython widget to interactively view molecular structures and trajectories in notebooks.
- plotly: Python interactive graphing library integrated in Jupyter notebooks.
- simpletraj: Lightweight coordinate-only trajectory reader based on code from GROMACS, MDAnalysis and VMD.
Conda Installation and Launch
git clone https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_wf_md_setup.git
cd biobb_wf_md_setup
conda env create -f conda_env/environment.yml
conda activate biobb_wf_md_setup
jupyter-notebook biobb_wf_md_setup/notebooks/biobb_wf_md_setup.ipynb
Pipeline steps
- Input Parameters
- Fetching PDB Structure
- Fix Protein Structure
- Create Protein System Topology
- Create Solvent Box
- Fill the Box with Water Molecules
- Adding Ions
- Energetically Minimize the System
- Equilibrate the System (NVT)
- Equilibrate the System (NPT)
- Free Molecular Dynamics Simulation
- Post-processing and Visualizing Resulting 3D Trajectory
- Output Files
- Questions & Comments

Initializing colab
The two cells below are used only in case this notebook is executed via Google Colab. Take into account that, for running conda on Google Colab, the condacolab library must be installed. As explained here, the installation requires a kernel restart, so when running this notebook in Google Colab, don't run all cells until this installation is properly finished and the kernel has restarted.
# Only executed when using google colab
import sys
if 'google.colab' in sys.modules:
import subprocess
from pathlib import Path
try:
subprocess.run(["conda", "-V"], check=True)
except FileNotFoundError:
subprocess.run([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", "condacolab"], check=True)
import condacolab
condacolab.install()
# Clone repository
repo_URL = "https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_wf_md_setup.git"
repo_name = Path(repo_URL).name.split('.')[0]
if not Path(repo_name).exists():
subprocess.run(["mamba", "install", "-y", "git"], check=True)
subprocess.run(["git", "clone", repo_URL], check=True)
print("⏬ Repository properly cloned.")
# Install environment
print("⏳ Creating environment...")
env_file_path = f"{repo_name}/conda_env/environment.yml"
subprocess.run(["mamba", "env", "update", "-n", "base", "-f", env_file_path], check=True)
print("🎨 Install NGLView dependencies...")
subprocess.run(["mamba", "install", "-y", "-c", "conda-forge", "nglview==3.0.8", "ipywidgets=7.7.2"], check=True)
print("👍 Conda environment successfully created and updated.")
# Enable widgets for colab
if 'google.colab' in sys.modules:
from google.colab import output
output.enable_custom_widget_manager()
# Change working dir
import os
os.chdir("biobb_wf_md_setup/biobb_wf_md_setup/notebooks")
print(f"📂 New working directory: {os.getcwd()}")
Input parameters
Input parameters needed:
- pdbCode: PDB code of the protein structure (e.g. 1AKI, https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb1AKI/pdb)
import nglview
import ipywidgets
import sys
pdbCode = "1AKI"
Fetching PDB structure
Downloading PDB structure with the protein molecule from the RCSB PDB database.
Alternatively, a PDB file can be used as starting structure.
Building Blocks used:
- Pdb from biobb_io.api.pdb
# Downloading desired PDB file
# Import module
from biobb_io.api.pdb import pdb
# Create properties dict and inputs/outputs
downloaded_pdb = pdbCode+'.pdb'
prop = {
'pdb_code': pdbCode
}
#Create and launch bb
pdb(output_pdb_path=downloaded_pdb,
properties=prop)
# Show protein
view = nglview.show_structure_file(downloaded_pdb)
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='all')
view._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','600px'])
view

Fix protein structure
Checking and fixing (if needed) the protein structure:
-
Modeling missing side-chain atoms, modifying incorrect amide assignments, choosing alternative locations.
- Checking for missing backbone atoms, heteroatoms, modified residues and possible atomic clashes.
Building Blocks used:
- FixSideChain from biobb_model.model.fix_side_chain
# Check & Fix PDB
# Import module
from biobb_model.model.fix_side_chain import fix_side_chain
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
fixed_pdb = pdbCode + '_fixed.pdb'
# Create and launch bb
fix_side_chain(input_pdb_path=downloaded_pdb,
output_pdb_path=fixed_pdb)
# Show protein
view = nglview.show_structure_file(fixed_pdb)
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='all')
view._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','600px'])
view.camera='orthographic'
view

Create protein system topology
Building GROMACS topology corresponding to the protein structure.
Force field used in this tutorial is amber99sb-ildn: AMBER parm99 force field with corrections on backbone (sb) and side-chain torsion potentials (ildn). Water molecules type used in this tutorial is spc/e.
Adding hydrogen atoms if missing. Automatically identifying disulfide bridges.
Generating two output files:
- GROMACS structure (gro file)
-
GROMACS topology ZIP compressed file containing:
- GROMACS topology top file (top file)
- GROMACS position restraint file/s (itp file/s)
Building Blocks used:
- Pdb2gmx from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.pdb2gmx
# Create system topology
# Import module
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.pdb2gmx import pdb2gmx
# Create inputs/outputs
output_pdb2gmx_gro = pdbCode+'_pdb2gmx.gro'
output_pdb2gmx_top_zip = pdbCode+'_pdb2gmx_top.zip'
# Create and launch bb
pdb2gmx(input_pdb_path=fixed_pdb,
output_gro_path=output_pdb2gmx_gro,
output_top_zip_path=output_pdb2gmx_top_zip)
# Show protein
view = nglview.show_structure_file(output_pdb2gmx_gro)
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='all')
view._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','600px'])
view.camera='orthographic'
view

Create solvent box
Define the unit cell for the protein structure MD system to fill it with water molecules.
A cubic box is used to define the unit cell, with a distance from the protein to the box edge of 1.0 nm. The protein is centered in the box.
Building Blocks used:
- Editconf from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.editconf
# Editconf: Create solvent box
# Import module
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.editconf import editconf
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_editconf_gro = pdbCode+'_editconf.gro'
prop = {
'box_type': 'cubic',
'distance_to_molecule': 1.0
}
#Create and launch bb
editconf(input_gro_path=output_pdb2gmx_gro,
output_gro_path=output_editconf_gro,
properties=prop)
Fill the box with water molecules
Fill the unit cell for the protein structure system with water molecules.
The solvent type used is the default Simple Point Charge water (SPC), a generic equilibrated 3-point solvent model.
Building Blocks used:
- Solvate from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.solvate
# Solvate: Fill the box with water molecules
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.solvate import solvate
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_solvate_gro = pdbCode+'_solvate.gro'
output_solvate_top_zip = pdbCode+'_solvate_top.zip'
# Create and launch bb
solvate(input_solute_gro_path=output_editconf_gro,
output_gro_path=output_solvate_gro,
input_top_zip_path=output_pdb2gmx_top_zip,
output_top_zip_path=output_solvate_top_zip)
# Show protein
view = nglview.show_structure_file(output_solvate_gro)
view.clear_representations()
view.add_representation(repr_type='cartoon', selection='solute', color='green')
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='SOL')
view._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','600px'])
view.camera='orthographic'
view

# Grompp: Creating portable binary run file for ion generation
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.grompp import grompp
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_gppion_tpr = pdbCode+'_gppion.tpr'
prop = {
'simulation_type': 'ions',
'maxwarn': 1
}
# Create and launch bb
grompp(input_gro_path=output_solvate_gro,
input_top_zip_path=output_solvate_top_zip,
output_tpr_path=output_gppion_tpr,
properties=prop)
# Genion: Adding ions to neutralize the system
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.genion import genion
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_genion_gro = pdbCode+'_genion.gro'
output_genion_top_zip = pdbCode+'_genion_top.zip'
prop={
'neutral':True
'concentration':0
}
# Create and launch bb
genion(input_tpr_path=output_gppion_tpr,
output_gro_path=output_genion_gro,
input_top_zip_path=output_solvate_top_zip,
output_top_zip_path=output_genion_top_zip,
properties=prop)
# Show protein
view = nglview.show_structure_file(output_genion_gro)
view.clear_representations()
view.add_representation(repr_type='cartoon', selection='solute', color='sstruc')
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='NA')
view.add_representation(repr_type='ball+stick', selection='CL')
view._remote_call('setSize', target='Widget', args=['','600px'])
view.camera='orthographic'
view

Energetically minimize the system
Energetically minimize the protein system till reaching a desired potential energy.
- Step 1: Creating portable binary run file for energy minimization
- Step 2: Energetically minimize the system till reaching a force of 500 kJ/mol*nm.
- Step 3: Checking energy minimization results. Plotting energy by time during the minimization process.
Building Blocks used:
- Grompp from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.grompp
- Mdrun from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.mdrun
- GMXEnergy from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_energy
Step 1: Creating portable binary run file for energy minimization
The minimization type of the molecular dynamics parameters (mdp) property contains the main default parameters to run an energy minimization:
- integrator = steep ; Algorithm (steep = steepest descent minimization)
- emtol = 1000.0 ; Stop minimization when the maximum force < 1000.0 kJ/mol/nm
- emstep = 0.01 ; Minimization step size (nm)
- nsteps = 50000 ; Maximum number of (minimization) steps to perform
In this particular example, the method used to run the energy minimization is the default steepest descent, but the maximum force is placed at 500 kJ/mol*nm^2, and the maximum number of steps to perform (if the maximum force is not reached) to 5,000 steps.
# Grompp: Creating portable binary run file for mdrun
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.grompp import grompp
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_gppmin_tpr = pdbCode+'_gppmin.tpr'
prop = {
'mdp':{
'emtol':'500',
'nsteps':'5000'
},
'simulation_type': 'minimization'
}
# Create and launch bb
grompp(input_gro_path=output_genion_gro,
input_top_zip_path=output_genion_top_zip,
output_tpr_path=output_gppmin_tpr,
properties=prop)
# Mdrun: Running minimization
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.mdrun import mdrun
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_min_trr = pdbCode+'_min.trr'
output_min_gro = pdbCode+'_min.gro'
output_min_edr = pdbCode+'_min.edr'
output_min_log = pdbCode+'_min.log'
# Create and launch bb
mdrun(input_tpr_path=output_gppmin_tpr,
output_trr_path=output_min_trr,
output_gro_path=output_min_gro,
output_edr_path=output_min_edr,
output_log_path=output_min_log)
# GMXEnergy: Getting system energy by time
from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_energy import gmx_energy
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_min_ene_xvg = pdbCode+'_min_ene.xvg'
prop = {
'terms': ["Potential"]
}
# Create and launch bb
gmx_energy(input_energy_path=output_min_edr,
output_xvg_path=output_min_ene_xvg,
properties=prop)
import plotly.graph_objs as go
# Read data from file and filter energy values higher than 1000 kJ/mol
with open(output_min_ene_xvg, 'r') as energy_file:
x, y = zip(*[
(float(line.split()[0]), float(line.split()[1]))
for line in energy_file
if not line.startswith(("#", "@"))
if float(line.split()[1]) < 1000
])
# Create a scatter plot
fig = go.Figure(data=go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode='lines'))
# Update layout
fig.update_layout(title="Energy Minimization",
xaxis_title="Energy Minimization Step",
yaxis_title="Potential Energy kJ/mol",
height=600)
# Show the figure (renderer changes for colab and jupyter)
rend = 'colab' if 'google.colab' in sys.modules else ''
fig.show(renderer=rend)

Equilibrate the system (NVT)
Equilibrate the protein system in NVT ensemble (constant Number of particles, Volume and Temperature). Protein heavy atoms will be restrained using position restraining forces: movement is permitted, but only after overcoming a substantial energy penalty. The utility of position restraints is that they allow us to equilibrate our solvent around our protein, without the added variable of structural changes in the protein.
- Step 1: Creating portable binary run file for system equilibration
- Step 2: Equilibrate the protein system with NVT ensemble.
- Step 3: Checking NVT Equilibration results. Plotting system temperature by time during the NVT equilibration process.
Building Blocks used:
- Grompp from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.grompp
- Mdrun from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.mdrun
- GMXEnergy from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_energy
Step 1: Creating portable binary run file for system equilibration (NVT)
The nvt type of the molecular dynamics parameters (mdp) property contains the main default parameters to run an NVT equilibration with protein restraints (see GROMACS mdp options):
- Define = -DPOSRES
- integrator = md
- dt = 0.002
- nsteps = 5000
- pcoupl = no
- gen_vel = yes
- gen_temp = 300
- gen_seed = -1
In this particular example, the default parameters will be used: md integrator algorithm, a step size of 2fs, 5,000 equilibration steps with the protein heavy atoms restrained, and a temperature of 300K.
Please note that for the sake of time this tutorial is only running 10ps of NVT equilibration, whereas in the original example the simulated time was 100ps.
# Grompp: Creating portable binary run file for NVT Equilibration
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.grompp import grompp
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_gppnvt_tpr = pdbCode+'_gppnvt.tpr'
prop = {
'mdp':{
'nsteps': 5000,
'dt': 0.002,
'Define': '-DPOSRES',
#'tc_grps': "DNA Water_and_ions" # NOTE: uncomment this line if working with DNA
},
'simulation_type': 'nvt'
}
# Create and launch bb
grompp(input_gro_path=output_min_gro,
input_top_zip_path=output_genion_top_zip,
output_tpr_path=output_gppnvt_tpr,
properties=prop)
# Mdrun: Running Equilibration NVT
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.mdrun import mdrun
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_nvt_trr = pdbCode+'_nvt.trr'
output_nvt_gro = pdbCode+'_nvt.gro'
output_nvt_edr = pdbCode+'_nvt.edr'
output_nvt_log = pdbCode+'_nvt.log'
output_nvt_cpt = pdbCode+'_nvt.cpt'
# Create and launch bb
mdrun(input_tpr_path=output_gppnvt_tpr,
output_trr_path=output_nvt_trr,
output_gro_path=output_nvt_gro,
output_edr_path=output_nvt_edr,
output_log_path=output_nvt_log,
output_cpt_path=output_nvt_cpt)
# GMXEnergy: Getting system temperature by time during NVT Equilibration
from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_energy import gmx_energy
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_nvt_temp_xvg = pdbCode+'_nvt_temp.xvg'
prop = {
'terms': ["Temperature"]
}
# Create and launch bb
gmx_energy(input_energy_path=output_nvt_edr,
output_xvg_path=output_nvt_temp_xvg,
properties=prop)
import plotly.graph_objs as go
# Read temperature data from file
with open(output_nvt_temp_xvg, 'r') as temperature_file:
x, y = zip(*[
(float(line.split()[0]), float(line.split()[1]))
for line in temperature_file
if not line.startswith(("#", "@"))
])
# Create a scatter plot
fig = go.Figure(data=go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode='lines+markers'))
# Update layout
fig.update_layout(title="Temperature during NVT Equilibration",
xaxis_title="Time (ps)",
yaxis_title="Temperature (K)",
height=600)
# Show the figure (renderer changes for colab and jupyter)
rend = 'colab' if 'google.colab' in sys.modules else ''
fig.show(renderer=rend)

Equilibrate the system (NPT)
Equilibrate the protein system in NPT ensemble (constant Number of particles, Pressure and Temperature).
- Step 1: Creating portable binary run file for system equilibration
- Step 2: Equilibrate the protein system with NPT ensemble.
- Step 3: Checking NPT Equilibration results. Plotting system pressure and density by time during the NPT equilibration process.
Building Blocks used:
- Grompp from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.grompp
- Mdrun from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.mdrun
- GMXEnergy from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_energy
Step 1: Creating portable binary run file for system equilibration (NPT)
The npt type of the molecular dynamics parameters (mdp) property contains the main default parameters to run an NPT equilibration with protein restraints (see GROMACS mdp options):
- Define = -DPOSRES
- integrator = md
- dt = 0.002
- nsteps = 5000
- pcoupl = Parrinello-Rahman
- pcoupltype = isotropic
- tau_p = 1.0
- ref_p = 1.0
- compressibility = 4.5e-5
- refcoord_scaling = com
- gen_vel = no
In this particular example, the default parameters will be used: md integrator algorithm, a time step of 2fs, 5,000 equilibration steps with the protein heavy atoms restrained, and a Parrinello-Rahman pressure coupling algorithm.
Please note that for the sake of time this tutorial is only running 10ps of NPT equilibration, whereas in the original example the simulated time was 100ps.
# Grompp: Creating portable binary run file for NPT System Equilibration
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.grompp import grompp
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_gppnpt_tpr = pdbCode+'_gppnpt.tpr'
prop = {
'mdp':{
'nsteps':'5000',
#'tc_grps': "DNA Water_and_ions" # NOTE: uncomment this line if working with DNA
},
'simulation_type': 'npt'
}
# Create and launch bb
grompp(input_gro_path=output_nvt_gro,
input_top_zip_path=output_genion_top_zip,
output_tpr_path=output_gppnpt_tpr,
input_cpt_path=output_nvt_cpt,
properties=prop)
# Mdrun: Running NPT System Equilibration
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.mdrun import mdrun
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_npt_trr = pdbCode+'_npt.trr'
output_npt_gro = pdbCode+'_npt.gro'
output_npt_edr = pdbCode+'_npt.edr'
output_npt_log = pdbCode+'_npt.log'
output_npt_cpt = pdbCode+'_npt.cpt'
# Create and launch bb
mdrun(input_tpr_path=output_gppnpt_tpr,
output_trr_path=output_npt_trr,
output_gro_path=output_npt_gro,
output_edr_path=output_npt_edr,
output_log_path=output_npt_log,
output_cpt_path=output_npt_cpt)
# GMXEnergy: Getting system pressure and density by time during NPT Equilibration
from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_energy import gmx_energy
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_npt_pd_xvg = pdbCode+'_npt_PD.xvg'
prop = {
'terms': ["Pressure","Density"]
}
# Create and launch bb
gmx_energy(input_energy_path=output_npt_edr,
output_xvg_path=output_npt_pd_xvg,
properties=prop)
import plotly.graph_objs as go
from plotly.subplots import make_subplots
# Read pressure and density data from file
with open(output_npt_pd_xvg,'r') as pd_file:
x, y, z = zip(*[
(float(line.split()[0]), float(line.split()[1]), float(line.split()[2]))
for line in pd_file
if not line.startswith(("#", "@"))
])
trace1 = go.Scatter(
x=x,y=y
)
trace2 = go.Scatter(
x=x,y=z
)
fig = make_subplots(rows=1, cols=2, print_grid=False)
fig.append_trace(trace1, 1, 1)
fig.append_trace(trace2, 1, 2)
fig.update_layout(
height=500,
title='Pressure and Density during NPT Equilibration',
showlegend=False,
xaxis1_title='Time (ps)',
yaxis1_title='Pressure (bar)',
xaxis2_title='Time (ps)',
yaxis2_title='Density (Kg*m^-3)'
)
# Show the figure (renderer changes for colab and jupyter)
rend = 'colab' if 'google.colab' in sys.modules else ''
fig.show(renderer=rend)

Free Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Upon completion of the two equilibration phases (NVT and NPT), the system is now well-equilibrated at the desired temperature and pressure. The position restraints can now be released. The last step of the protein MD setup is a short, free MD simulation, to ensure the robustness of the system.
- Step 1: Creating portable binary run file to run a free MD simulation.
- Step 2: Run short MD simulation of the protein system.
- Step 3: Checking results for the final step of the setup process, the free MD run. Plotting Root Mean Square deviation (RMSd) and Radius of Gyration (Rgyr) by time during the free MD run step.
Building Blocks used:
- Grompp from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.grompp
- Mdrun from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.mdrun
- GMXRms from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_rms
- GMXRgyr from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_rgyr
Step 1: Creating portable binary run file to run a free MD simulation
The free type of the molecular dynamics parameters (mdp) property contains the main default parameters to run an free MD simulation (see GROMACS mdp options):
- integrator = md
- dt = 0.002 (ps)
- nsteps = 50000
In this particular example, the default parameters will be used: md integrator algorithm, a time step of 2fs, and a total of 50,000 md steps (100ps).
Please note that for the sake of time this tutorial is only running 100ps of free MD, whereas in the original example the simulated time was 1ns (1000ps).
# Grompp: Creating portable binary run file for mdrun
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.grompp import grompp
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_gppmd_tpr = pdbCode+'_gppmd.tpr'
prop = {
'mdp':{
'nsteps':'50000',
#'tc_grps': "DNA Water_and_ions" # NOTE: uncomment this line if working with DNA
},
'simulation_type': 'free'
}
# Create and launch bb
grompp(input_gro_path=output_npt_gro,
input_top_zip_path=output_genion_top_zip,
output_tpr_path=output_gppmd_tpr,
input_cpt_path=output_npt_cpt,
properties=prop)
# Mdrun: Running free dynamics
from biobb_gromacs.gromacs.mdrun import mdrun
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_md_trr = pdbCode+'_md.trr'
output_md_gro = pdbCode+'_md.gro'
output_md_edr = pdbCode+'_md.edr'
output_md_log = pdbCode+'_md.log'
output_md_cpt = pdbCode+'_md.cpt'
# Create and launch bb
mdrun(input_tpr_path=output_gppmd_tpr,
output_trr_path=output_md_trr,
output_gro_path=output_md_gro,
output_edr_path=output_md_edr,
output_log_path=output_md_log,
output_cpt_path=output_md_cpt)
Step 3: Checking free MD simulation results
Checking results for the final step of the setup process, the free MD run. Plotting Root Mean Square deviation (RMSd) and Radius of Gyration (Rgyr) by time during the free MD run step. RMSd against the experimental structure (input structure of the pipeline) and against the minimized and equilibrated structure (output structure of the NPT equilibration step).
# GMXRms: Computing Root Mean Square deviation to analyse structural stability
# RMSd against minimized and equilibrated snapshot (backbone atoms)
from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_rms import gmx_rms
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_rms_first = pdbCode+'_rms_first.xvg'
prop = {
'selection': 'Backbone',
#'selection': 'non-Water'
}
# Create and launch bb
gmx_rms(input_structure_path=output_gppmd_tpr,
input_traj_path=output_md_trr,
output_xvg_path=output_rms_first,
properties=prop)
# GMXRms: Computing Root Mean Square deviation to analyse structural stability
# RMSd against experimental structure (backbone atoms)
from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_rms import gmx_rms
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_rms_exp = pdbCode+'_rms_exp.xvg'
prop = {
'selection': 'Backbone',
#'selection': 'non-Water'
}
# Create and launch bb
gmx_rms(input_structure_path=output_gppmin_tpr,
input_traj_path=output_md_trr,
output_xvg_path=output_rms_exp,
properties=prop)
import plotly.graph_objs as go
# Read RMS vs first snapshot data from file
with open(output_rms_first,'r') as rms_first_file:
x, y = zip(*[
(float(line.split()[0]), float(line.split()[1]))
for line in rms_first_file
if not line.startswith(("#", "@"))
])
# Read RMS vs experimental structure data from file
with open(output_rms_exp,'r') as rms_exp_file:
x2, y2 = zip(*[
(float(line.split()[0]), float(line.split()[1]))
for line in rms_exp_file
if not line.startswith(("#", "@"))
])
fig = make_subplots()
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode="lines+markers", name="RMSd vs first"))
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(x=x, y=y2, mode="lines+markers", name="RMSd vs exp"))
# Set layout including height
fig.update_layout(
title="RMSd during free MD Simulation",
xaxis=dict(title="Time (ps)"),
yaxis=dict(title="RMSd (nm)"),
height=600
)
# Show the figure (renderer changes for colab and jupyter)
rend = 'colab' if 'google.colab' in sys.modules else ''
fig.show(renderer=rend)

# GMXRgyr: Computing Radius of Gyration to measure the protein compactness during the free MD simulation
from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_rgyr import gmx_rgyr
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_rgyr = pdbCode+'_rgyr.xvg'
prop = {
'selection': 'Backbone'
}
# Create and launch bb
gmx_rgyr(input_structure_path=output_gppmin_tpr,
input_traj_path=output_md_trr,
output_xvg_path=output_rgyr,
properties=prop)
import plotly.graph_objs as go
# Read Rgyr data from file
with open(output_rgyr, 'r') as rgyr_file:
x, y = zip(*[
(float(line.split()[0]), float(line.split()[1]))
for line in rgyr_file
if not line.startswith(("#", "@"))
])
# Create a scatter plot
fig = go.Figure(data=go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode='lines+markers'))
# Update layout
fig.update_layout(title="Radius of Gyration",
xaxis_title="Time (ps)",
yaxis_title="Rgyr (nm)",
height=600)
# Show the figure (renderer changes for colab and jupyter)
rend = 'colab' if 'google.colab' in sys.modules else ''
fig.show(renderer=rend)

Post-processing and Visualizing resulting 3D trajectory
Post-processing and Visualizing the protein system MD setup resulting trajectory using NGL
- Step 1: Imaging the resulting trajectory, stripping out water molecules and ions and correcting periodicity issues.
- Step 2: Generating a dry structure, removing water molecules and ions from the final snapshot of the MD setup pipeline.
- Step 3: Visualizing the imaged trajectory using the dry structure as a topology.
Building Blocks used:
- GMXImage from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_image
- GMXTrjConvStr from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_trjconv_str
# GMXImage: "Imaging" the resulting trajectory
# Removing water molecules and ions from the resulting structure
from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_image import gmx_image
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_imaged_traj = pdbCode+'_imaged_traj.trr'
prop = {
'center_selection': 'Protein',
'output_selection': 'Protein',
'pbc' : 'mol',
'center' : True
}
# Create and launch bb
gmx_image(input_traj_path=output_md_trr,
input_top_path=output_gppmd_tpr,
output_traj_path=output_imaged_traj,
properties=prop)
# GMXTrjConvStr: Converting and/or manipulating a structure
# Removing water molecules and ions from the resulting structure
# The "dry" structure will be used as a topology to visualize
# the "imaged dry" trajectory generated in the previous step.
from biobb_analysis.gromacs.gmx_trjconv_str import gmx_trjconv_str
# Create prop dict and inputs/outputs
output_dry_gro = pdbCode+'_md_dry.gro'
prop = {
'selection': 'Protein'
}
# Create and launch bb
gmx_trjconv_str(input_structure_path=output_md_gro,
input_top_path=output_gppmd_tpr,
output_str_path=output_dry_gro,
properties=prop)
Step 3: Visualizing the generated dehydrated trajectory.
Using the imaged trajectory (output of the Post-processing step 1) with the dry structure (output of the Post-processing step 2) as a topology.
# Show trajectory
view = nglview.show_simpletraj(nglview.SimpletrajTrajectory(output_imaged_traj, output_dry_gro), gui=True)
view
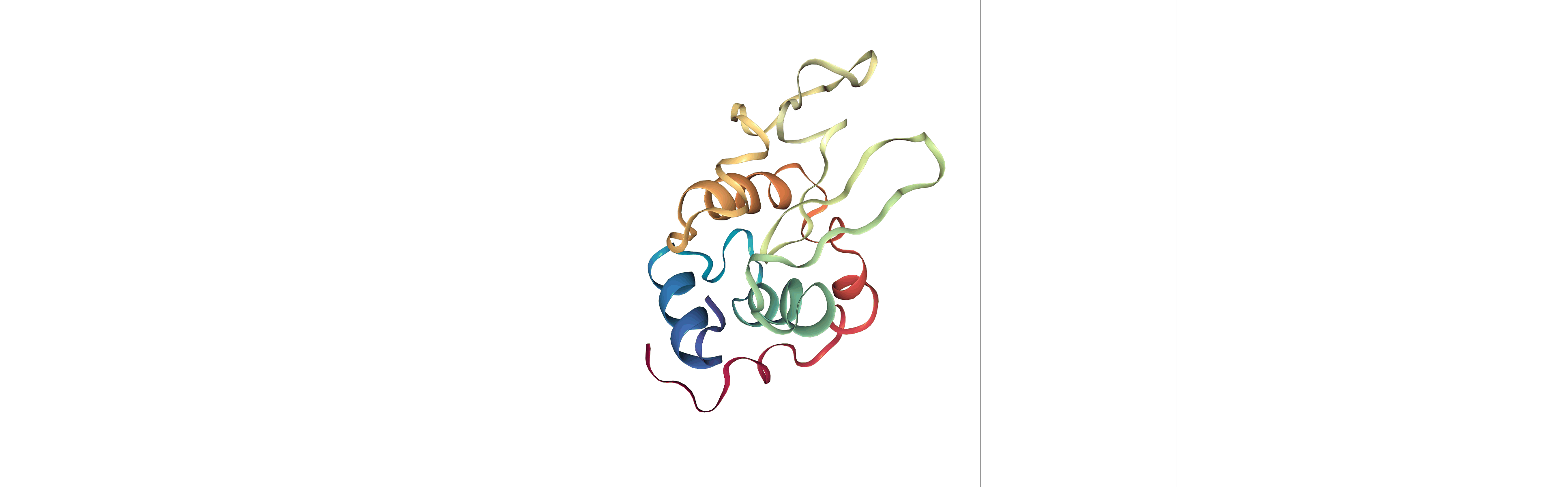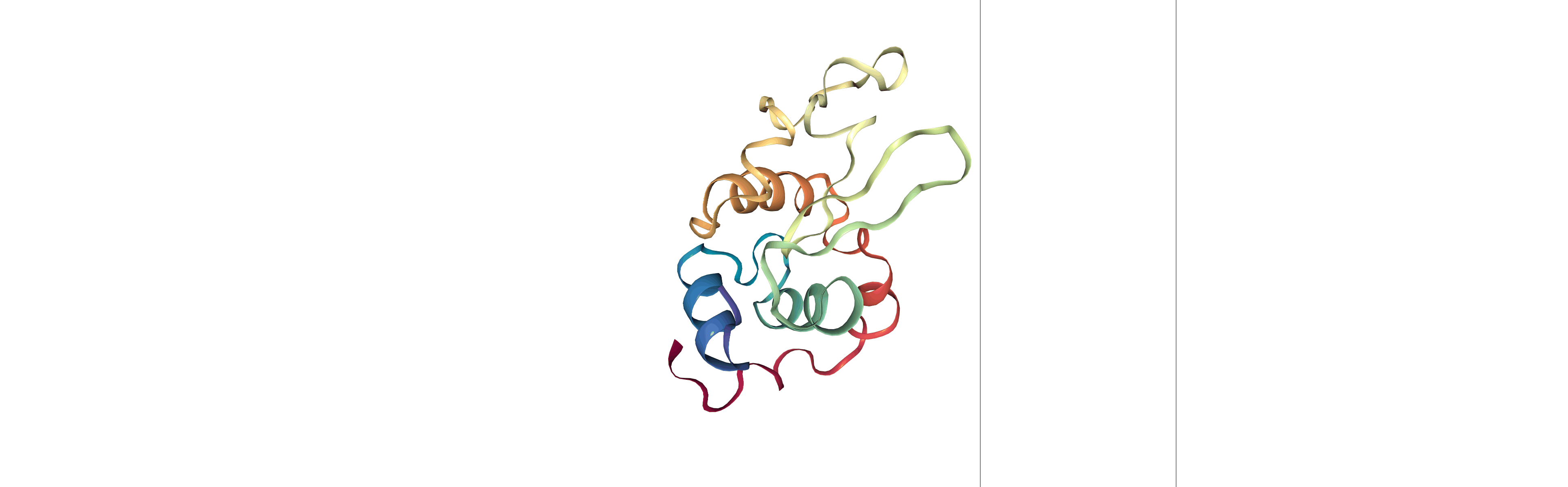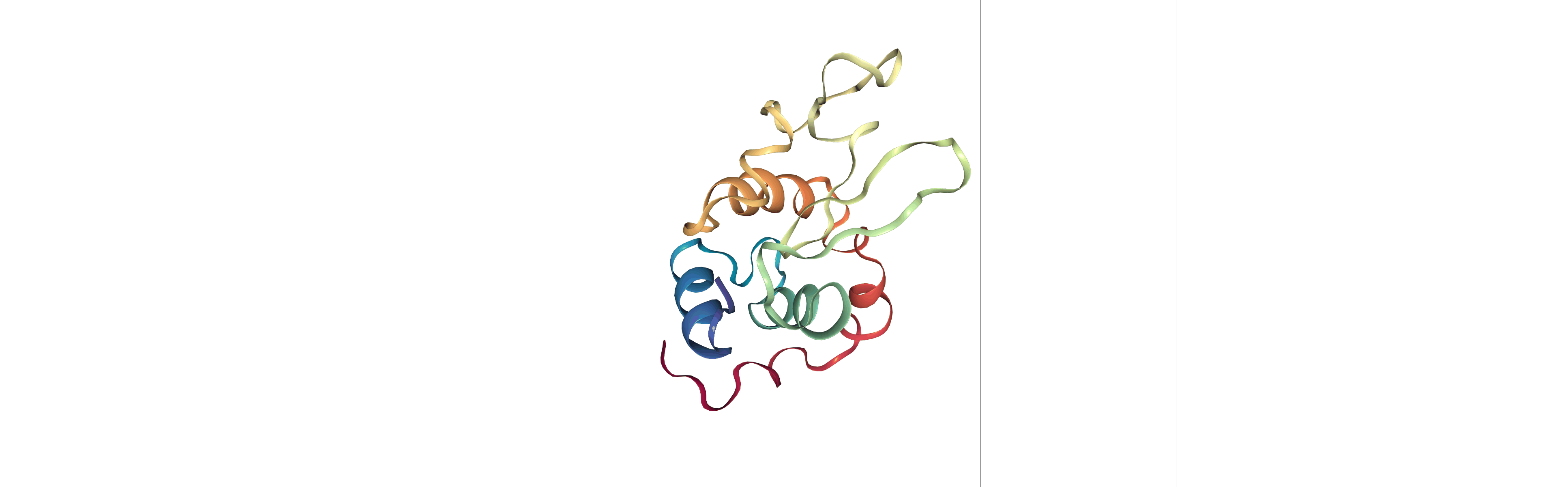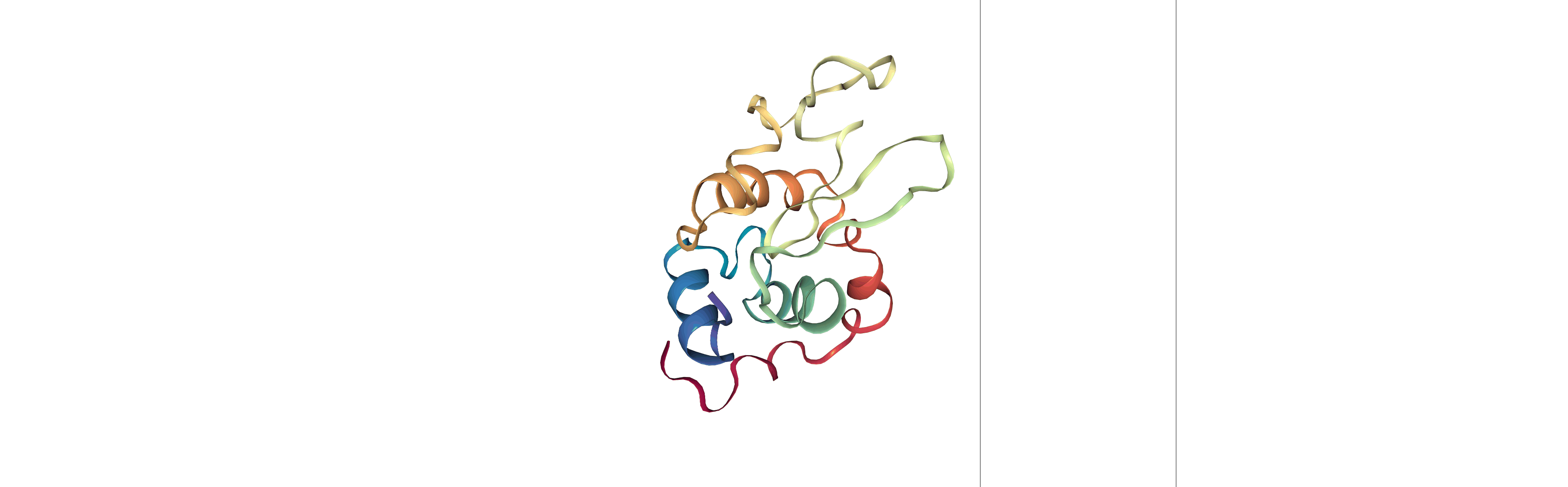
Output files
Important Output files generated:
- output_md_gro (1AKI_md.gro): Final structure (snapshot) of the MD setup protocol.
- output_md_trr (1AKI_md.trr): Final trajectory of the MD setup protocol.
- output_md_cpt (1AKI_md.cpt): Final checkpoint file, with information about the state of the simulation. It can be used to restart or continue a MD simulation.
- output_gppmd_tpr (1AKI_gppmd.tpr): Final tpr file, GROMACS portable binary run input file. This file contains the starting structure of the MD setup free MD simulation step, together with the molecular topology and all the simulation parameters. It can be used to extend the simulation.
- output_genion_top_zip (1AKI_genion_top.zip): Final topology of the MD system. It is a compressed zip file including a topology file (.top) and a set of auxiliary include topology files (.itp).
Analysis (MD setup check) output files generated:
- output_rms_first (1AKI_rms_first.xvg): Root Mean Square deviation (RMSd) against minimized and equilibrated structure of the final free MD run step.
- output_rms_exp (1AKI_rms_exp.xvg): Root Mean Square deviation (RMSd) against experimental structure of the final free MD run step.
- output_rgyr (1AKI_rgyr.xvg): Radius of Gyration of the final free MD run step of the setup pipeline.
