MC DNA Help - Analysis Curves
Using Curves+, MC DNA offers a complete study of Nucleic Acids Helical Parameters:
- Axis Base Pairs :: Method - Results
- Inter-Base Pairs :: Method - Results
- Grooves :: Method - Results
Axis Base Pair
Method
Nucleotide Base pairs, the DNA building blocks, are made of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds.
The major elements of flexibility in the DNA base pairs when we consider them as a blocks (movements of the whole base pair) are divided in two types: Translational (x/y-displacement) and rotational (inclination, tip) parameters.
- X-displacement: Translation around the X-axis.
- Y-displacement: Translation around the Y-axis.
- Inclination: Rotation around the X-axis.
- Tip: Rotation around the Y-axis.

Results
Axis Base Pair analyses are shown in a set of line plots. The parameter value (or average value + standard deviation in case of structure ensemble) is represented with a yellow point-line (y-axis) for each of the nucleotides along the input sequence (x-axis). For the sake of comparison, a black point-line is also represented (whenever is available), showing the average values of the same parameter for the same base pair in the ABC MD study.
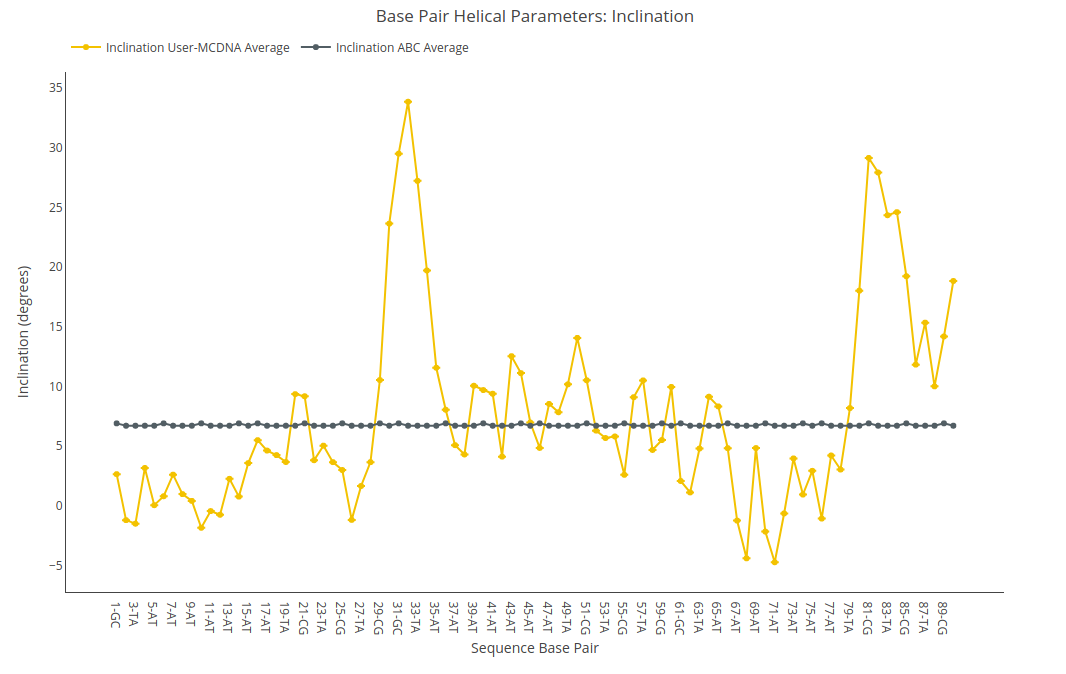
Inclination
Inclination value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the nucleotides in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Inclination value in degrees, X-axis: Sequence base pairs. Black point-line represents the ABC average values.
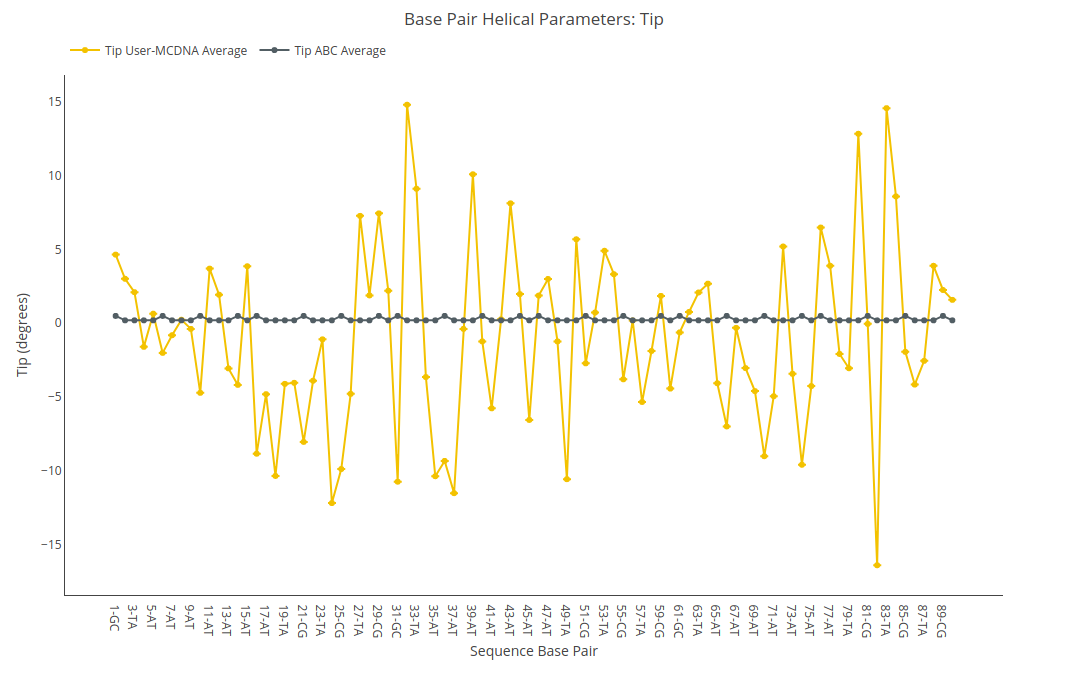
Tip
Tip value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the nucleotides in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Tip value in degrees, X-axis: Sequence base pairs. Black point-line represents the ABC average values.
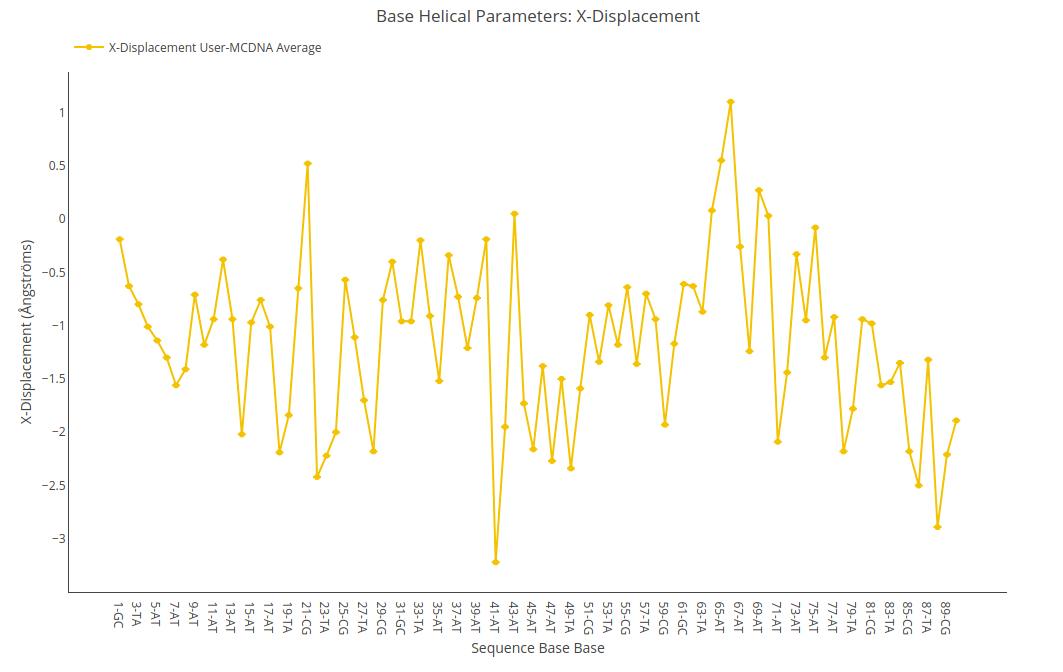
X-displacement
X-displacement value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the nucleotides in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: X-displacement value in Angstroms, X-axis: Sequence base pairs.
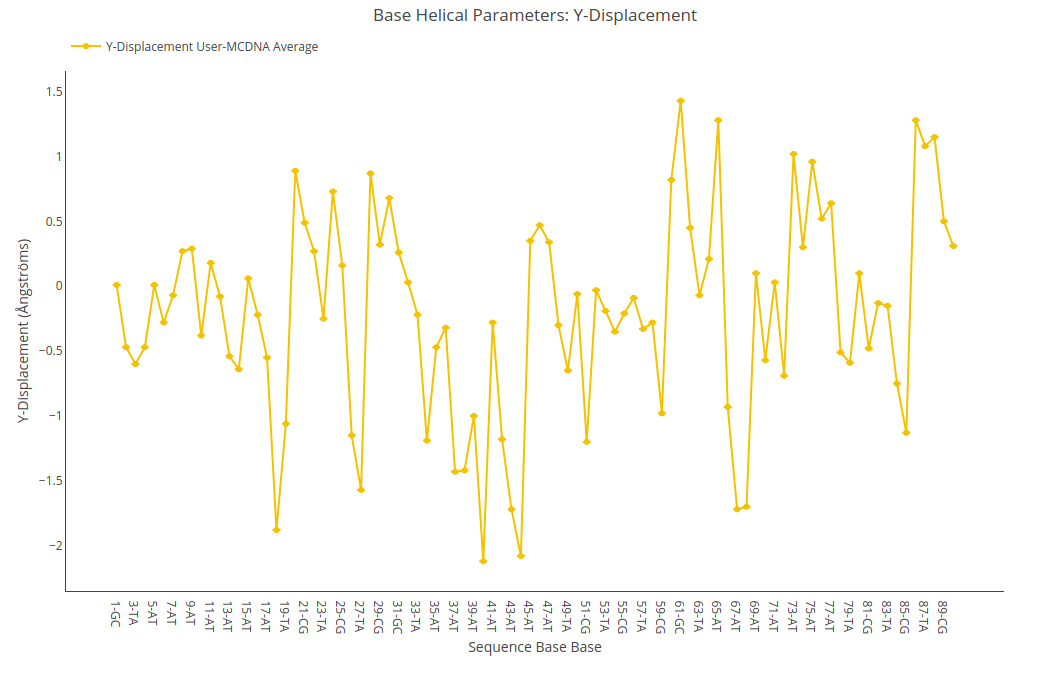
Y-displacement
Y-displacement value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the nucleotides in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Y-displacement value in Angstroms, X-axis: Sequence base pairs.
Inter Base Pair
Method
Nucleotide Base pair steps, build by two adjacent base pairs (two base pairs, four nucleotides -two from one strand, two from the other strand-), are the DNA blocks that characterize the helical structure of the molecule. Changes in the helical parameters (described in the following sections) of these base pair steps can be used to describe disruptions in a DNA structure.
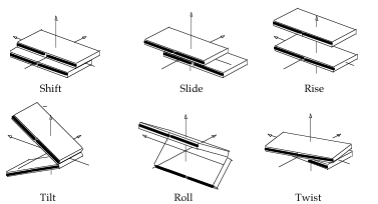
The major elements of flexibility in the DNA base pair steps when we consider them as a two elements interacting to each other (movements of a base pair with respect to adjacent base pair) can be divided again in two different types: Translational (Shift, Slide, Rise) and rotational (Tilt, Roll, Twist) parameters.
- Shift: Translation around the X-axis.
- Slide: Translation around the Y-axis.
- Rise: Translation around the Z-axis.
- Tilt: Rotation around the X-axis.
- Roll: Rotation around the Y-axis.
- Twist: Rotation around the Z-axis.
Results
Inter Base Pair analyses are shown in a set of line plots. The parameter value (or average value + standard deviation in case of structure ensemble) is represented with a yellow point-line (y-axis) for each of the base pair steps along the input sequence (x-axis). For the sake of comparison, a black and a red point-line are also represented, showing the average values of the same parameter for the same base pair in the ABC MD study, and in a compilation of experimental crystal structures from the PDB, respectively. Both set of values used for comparisons are extracted from the same work ( Dans et al., NAR 2012)
Shift
Shift value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Shift value in Angstroms, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps. Black point-line represents the ABC average values, whereas red point-line represents the experimental crystal structures average values.

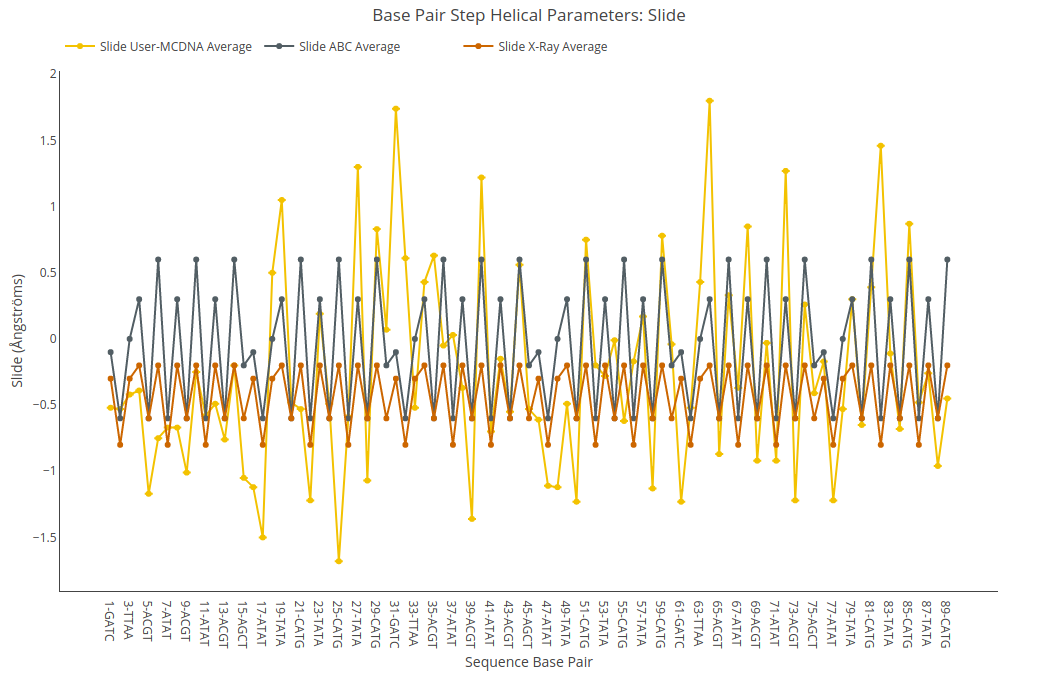
Slide
Slide value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Slide value in Angstroms, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps. Black point-line represents the ABC average values, whereas red point-line represents the experimental crystal structures average values.
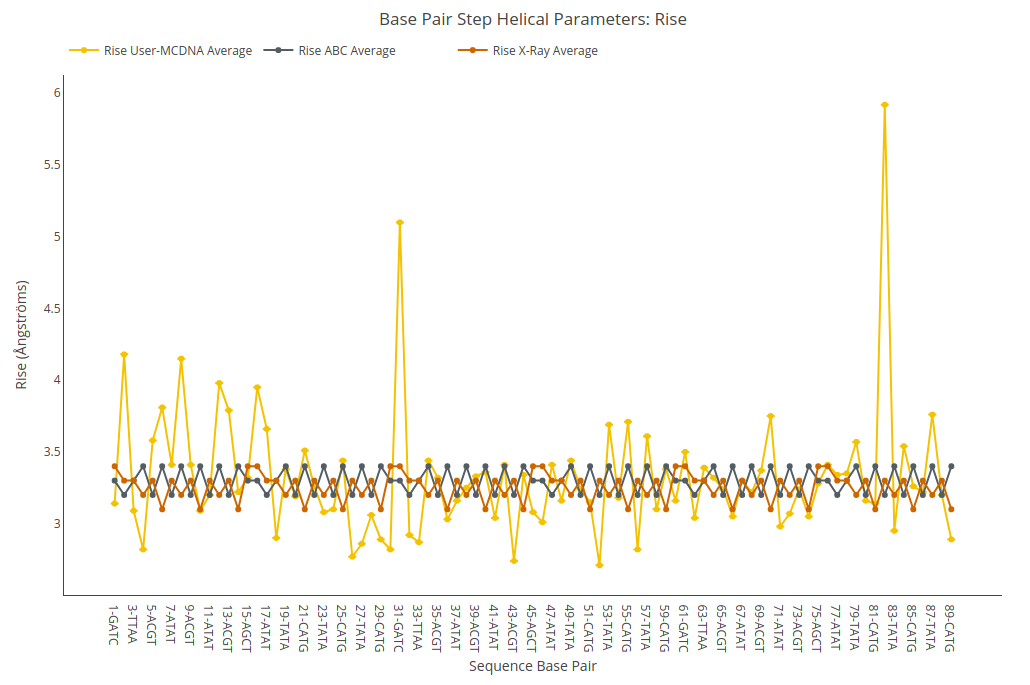
Rise
Rise value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Rise value in Angstroms, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps. Black point-line represents the ABC average values, whereas red point-line represents the experimental crystal structures average values.
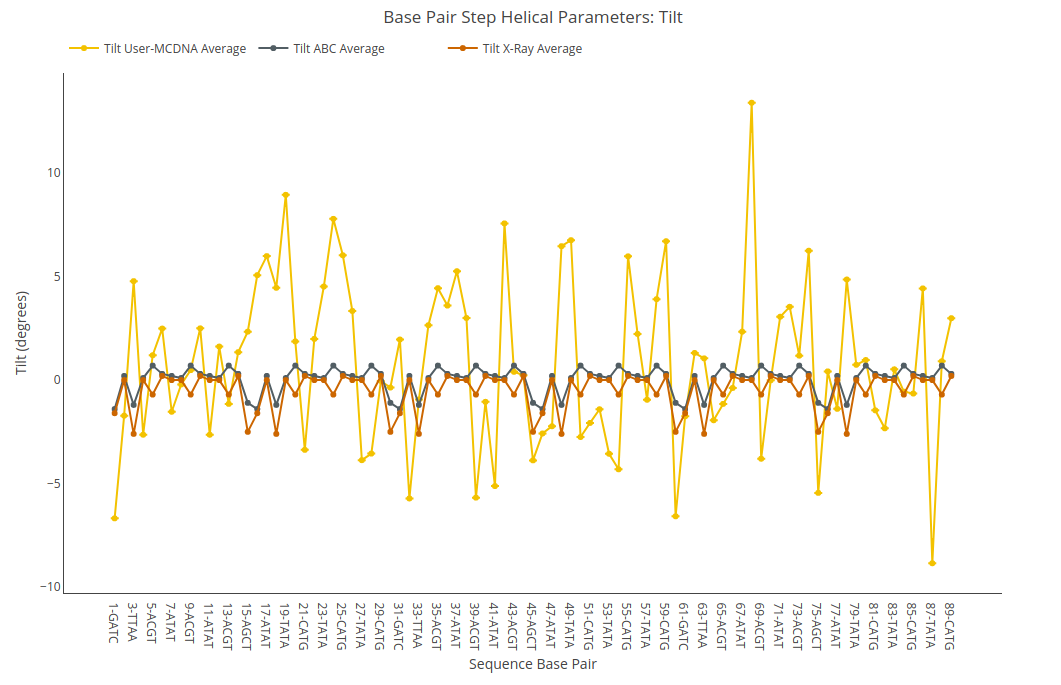
Tilt
Tilt value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Tilt value in degrees, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps. Black point-line represents the ABC average values, whereas red point-line represents the experimental crystal structures average values.
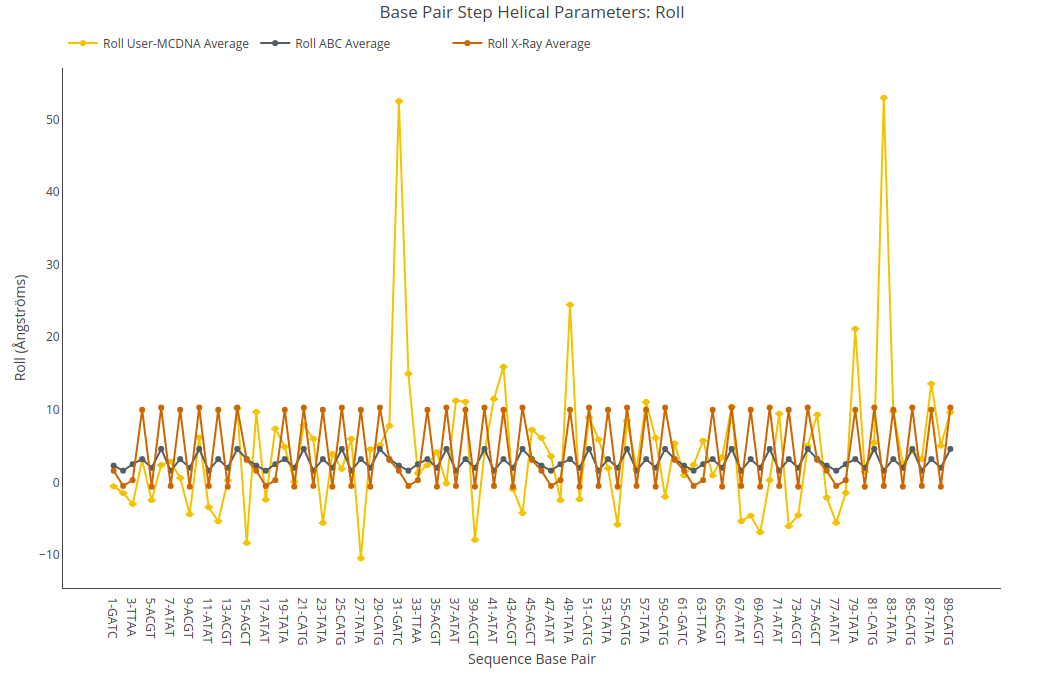
Roll
Roll value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Roll value in degrees, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps. Black point-line represents the ABC average values, whereas red point-line represents the experimental crystal structures average values.
Twist
Twist value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Twist value in degrees, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps. Black point-line represents the ABC average values, whereas red point-line represents the experimental crystal structures average values.

Grooves
Method
Nucleic Acid Structure's strand backbones appear closer together on one side of the helix than on the other. This creates a Major groove (where backbones are far apart) and a Minor groove (where backbones are close together). Depth and width of these grooves can be mesured giving information about the different conformations that the nucleic acid structure can achieve.
- Major Groove Width.
- Major Groove Depth.
- Minor Groove Width.
- Minor Groove Depth.
Results
Grooves analyses are shown in a set of line plots. The parameter value (or average value + standard deviation in case of structure ensemble) is represented with a yellow point-line (y-axis) for each of the base pair steps along the input sequence (x-axis).
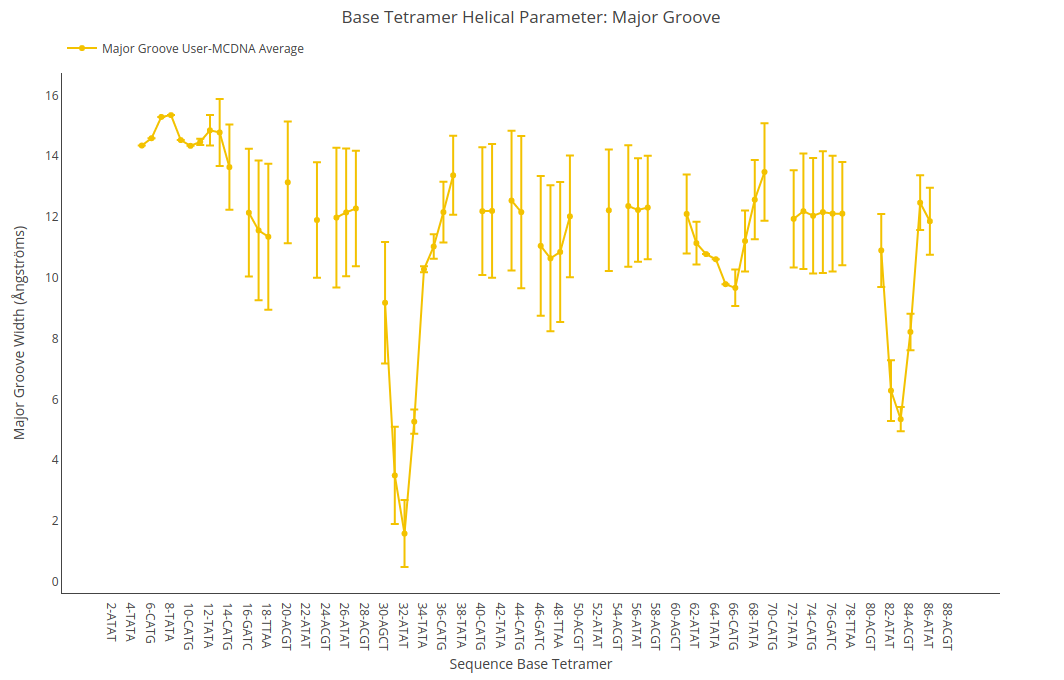
Major Groove Width
Major Groove Width value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Major Groove Width value in Angstroms, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps.
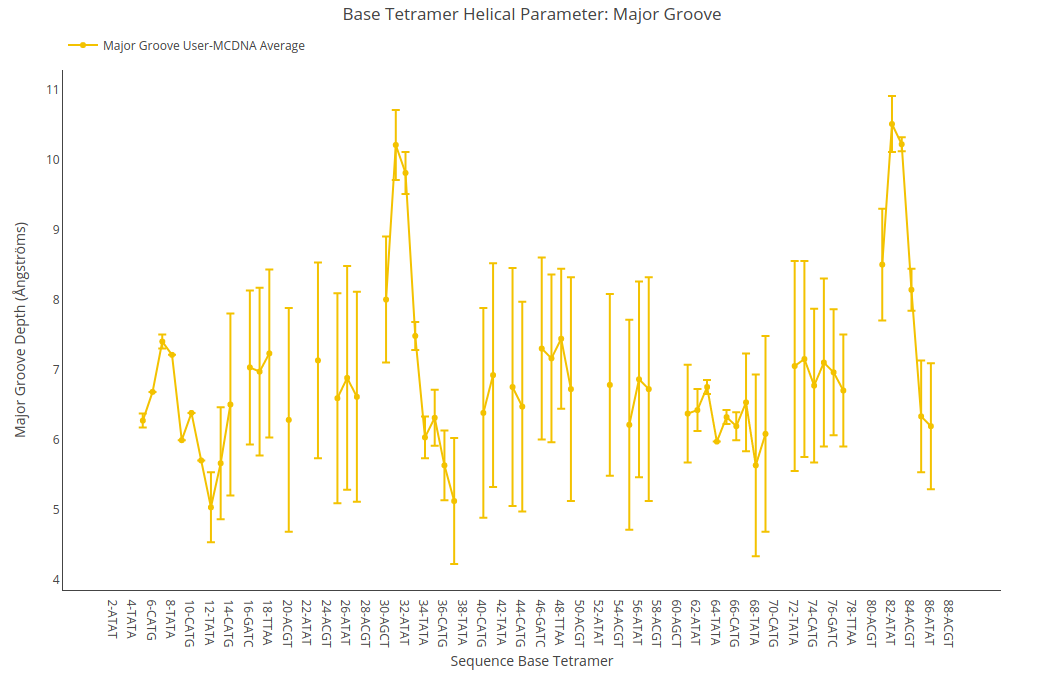
Major Groove Depth
Major Groove Depth value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Major Groove Depth value in Angstroms, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps.
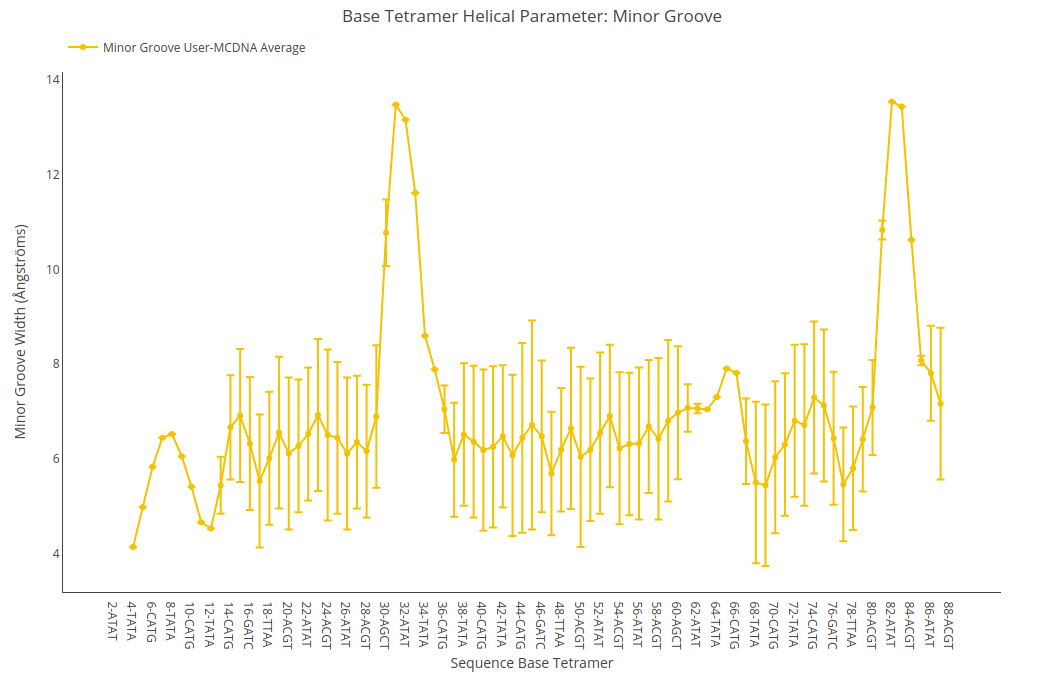
Minor Groove Width
Minor Groove Width value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Minor Groove Width value in Angstroms, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps.
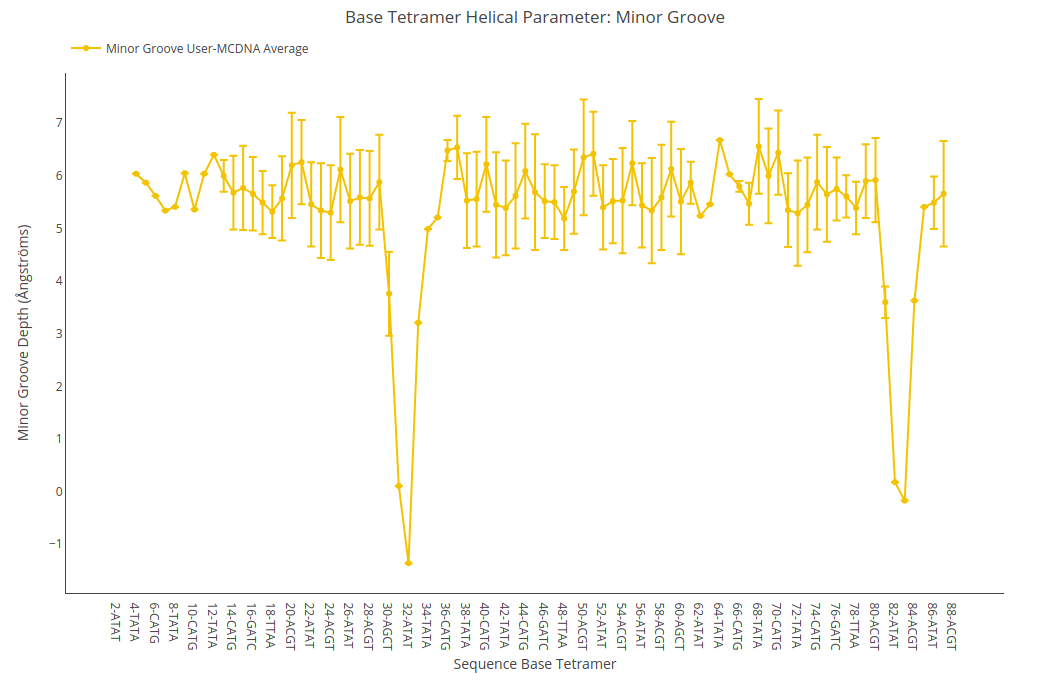
Minor Groove Depth
Minor Groove Depth value (for structure) or average value together with its associated standard deviation (for ensembles) is shown for each of the base pair steps in the sequence in a yellow point-line. Y-axis: Minor Groove Depth value in Angstroms, X-axis: Sequence base pair steps.